by Georges De Moura and Lydia Kostopoulos*
According to the engineer and entrepreneur Peter Diamandis, in the next ten years we are likely to experience as much technological change as in the past 100 years. The technologies of the fourth industrial revolution are set to become far more widespread and accessible. They will also converge in ways that create new value.
Companies and governments around the world are developing modernization strategies to use these new technologies, which include artificial intelligence, cloud-based services and internet of things. The success of any organization’s digital transformation, however, is not entirely dependent on state-of-the-art technology; it depends on human capital, too. This is one aspect of technological change management that persistently gets forgotten.
Human security as an after-thought
Security is often an after-thought in technological design and implementation, despite the grave threat cyber attacks pose to business continuity, service delivery and intellectual property protection. With the rise of more advanced encryption and security protocols, malicious actors have increasingly sought to compromise the weakest link – the human beings who interact with these systems. It is no surprise that ransomware attacks have increased threefold in just the first half of 2021. The cybersecurity skills gap becomes more acute as new technologies create more complex digital supply chains. Here are some key ways to increase human security:
1. Invest in new skills
According to the 2020 Forum’s Future of Jobs report, skills gaps in the local labour market and the inability to attract the right talent remain among the leading barriers to the adoption of new technologies. Building a future-proof workforce will depend on properly defining the skills needed, and providing opportunities for people to train. The cybersecurity sector needs a diverse range of experience, expertise and thinking to tackle the enormous challenges ahead.

While science and technology skills remain an important foundation, analytical skills are equally important in dealing with big data. Marketing and communication skills are also needed to work with business stakeholders, as are legal skills, when it comes to interpreting complex regulatory policies.
Solving the workforce challenge will require business leaders to rethink and define effective systems for upskilling individuals and capabilities. Building this workforce of the future will rely on partnerships between businesses, government agencies and academic institutions.
2. Security awareness as a core element of workplace upskilling
Today some new graduates are already finding that they need to upskill even at the beginning of their first job. Many companies have understood that the longevity of higher education is decreasing, and that in order to maintain relevant expertise in their workforce, they need to be proactive about upskilling. The American telecommunications company AT&T, for example, has dedicated $1 billion to upskilling and educating its workforce.
What is still lacking, however, is a prioritization of cybersecurity awareness. People outside the IT and cybersecurity functions need training in this area in order to make better decisions on the design, the operation and oversight of digital infrastructure. As organisations adopt new technology, software and digital processes they need a cybersecurity education plan to keep employees informed and aware of any dangers.
3. Hire personnel with a combination of technology expertise and mentoring capability
It is not enough to have a digital transformation plan that meets deadlines and budgets. It needs to be implemented in a way that is compatible to an organization’s culture. People are the most important assets in an organization, and as such it is important to consider where they sit in the different technology adopter categories.
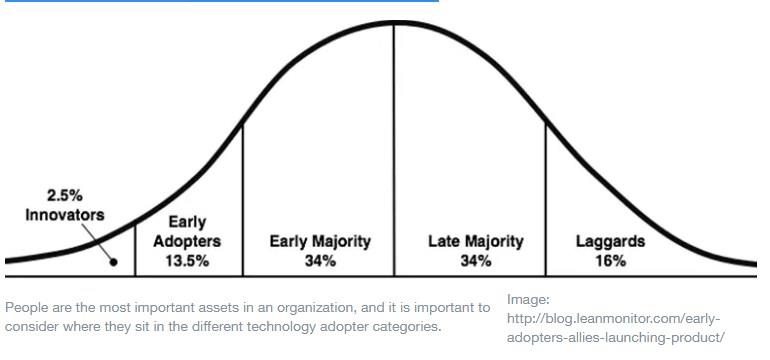
It is not uncommon for some people to resist technological change in their personal life or at work. There should be designated staff to facilitate technology education, and to offer coaching to staff during any technological transition. These people should be effective communicators who are versed in technological change management, technology and risk management. They need the right personality to support employees as they grapple with new technology and new risks.
The unprecedented growth of new technologies reminds us that our digital systems are an intractable part of the way business is done in the 21st century. These digital systems must include not only technical cybersecurity measures, but also a thoughtful analysis of the workforce’s skills and how it contributes to a sustainable culture of security.
*Head of Industry Solutions, Centre for Cybersecurity, World Economic Forum and SVP Emerging Tech Insights, Knowbe4, Inc.
**first published in: www.weforum.org




 By: N. Peter Kramer
By: N. Peter Kramer

