by Isabelle Durant*
This should be the time of year when people are packing suitcases and travel documents for their summer holidays – at least in the northern hemisphere. For many economies, these months are critical, and millions of businesses and workers are eager for tourists to return, especially given how badly the sector has already been hit.
Last year was catastrophic for tourism and the millions of people who depend on it. After six decades of extraordinary growth, the sector was brought to a near-complete standstill by the COVID-19 pandemic.
International tourist arrivals fell to levels not seen since 1990. We estimate that the crisis has cost the world about $4 trillion and placed over 100 million direct tourism jobs at risk. The impact is so big because of the numerous suppliers and businesses that are linked to the core sector. To put these numbers into perspective, the impact is almost equivalent to the GDP of France.
Slow progress
With vaccinations being rolled out in most developed economies, we would have expected the situation today to be significantly better than this time last year. Unfortunately, it is not.
So, what has happened? On the one hand, relatively slow progress in vaccination puts many tourism workers at risk, thus affecting the supply side. Tourism workers in developing economies, including destinations such as small island developing states, where tourism is a lifeline and a key driver of development, are particularly at risk.
On the other hand, travellers’ confidence is affected by the ever-changing travel restrictions that cannot be eased or lifted right now, particularly in light of new variants of the virus emerging and in the absence of sufficient roll-out of vaccinations.
Added to that, we have the costs of tests, a lack of coordination and clarity over regulations in place at destinations, limited international cooperation, the cancellation or rescheduling of flights, and general uncertainty about the evolution of the virus. It is small wonder so many people remain wary of travelling.
But tourists – and their money – are so needed right now. International tourism is a vital source of income for many countries. The foreign exchange earned through tourism is in many places a critical source for funds to finance public spending, investment for much-needed payment of relief and recovery measures, and for servicing debt repayments that have been piling up.
Tourism’s impact goes beyond economics. The sector is a key pillar of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, with a unique ability to contribute to most – if not all – of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals, including through providing opportunities for youth and women, and helping preserve and promote natural and cultural heritage.
Kickstarting the recovery
We are now less than 10 years away from our global goal of ensuring shared prosperity by 2030. The pandemic has put our joint progress on hold. We thus need urgent action. We need to kickstart tourism’s recovery for the millions who, for more than a year now, have been left struggling.
First and foremost, we need to collectively ensure that vaccination is equitably available across the world. One key concern is that developing countries, many of which are highly dependent on international tourism, are bearing the heaviest brunt of the uneven vaccination roll-out. Addressing this will require unprecedented levels of cooperation. However, while leaders have pledged their commitment to international solidarity, their words are yet to be backed up by actions.
On our side, the UN Conference on Trade and Development and the UN World Tourism Organization are leading the way in providing clear, updated and trusted data and analysis used by governments and businesses to inform recovery policies and decision-making.
Countries should also ensure that their tourism businesses of all sizes can survive the current crisis so that the power of the sector can be tapped when tourists return. This requires measures such as credit lines for tourism businesses and the provision of social protection for tourism workers.
In addition, digital technologies need to be used to increase security and boost travellers’ confidence. It is also time to step up digitalization among companies and the tourism workforce, upskilling the sector to become more resilient.
At the same time, we must look beyond the immediate restart of tourism. This crisis is an opportunity to rethink tourism. For instance, so-called “overtourism” had been a concern in many places prior to the pandemic.
Now is the moment to redesign and adjust tourism policies and management, including through greater diversification, more innovative products and the revitalisation of rural areas. Across the world, people have started to rediscover their own countries through domestic tourism and this offers an opportunity to spread the sector’s benefits more widely.
As we enter another peak travel season with the COVID-19 pandemic ongoing, we need to face up to the fact that the crisis confronting tourism is far from over.
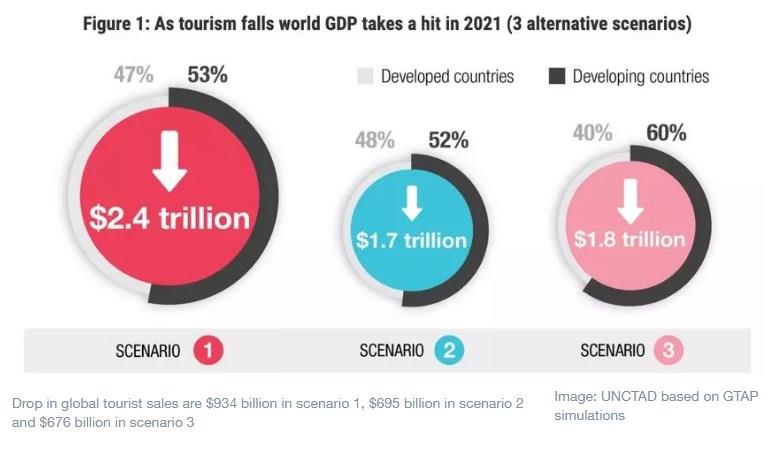
Last year, we set out three possible scenarios for the pandemic’s expected impact on the sector. The worst-case scenario turned out to be too optimistic. And this year, even in the most optimistic scenario, we will still be 60% below the levels of 2019.
But again, this should be seized as an opportunity to realign the sector towards greater sustainability and inclusivity rather than simply going back to the way we were before. Tourism is the sector with the broadest economic value chain and the deepest social footprint. Herein lies the opportunity to rethink, restart and to grow back better. But first, we need to restart tourism.
*Acting Secretary-General, UNCTAD
**first published in: www.weforum.org




 By: N. Peter Kramer
By: N. Peter Kramer

